



This article introduces the vacuum pump vacuum drying process for raw materials. Based on the characteristics of organic solvents, the limitations of traditional wet vacuum systems in recovering organic solvents were analyzed. Introduced the structure and advantages of dry vacuum pumps. The concept of dry vacuum condensation system was proposed, and the design and selection of system components (dry screw vacuum pump, vacuum pipeline, condenser, etc.) were introduced.
1. Overview
Raw materials that use solvent crystallization technology are usually filtered (solid-liquid separation), washed, and vacuum dried after crystallization. Common vacuum dryers include double cone dryers and integrated filtering, washing, and drying machines (three in one). The process of solid-liquid separation varies, and the moisture content of the material varies. The moisture content (dry basis) is usually between 20% and 200%. After drying, the moisture content (dry basis) of the finished raw material is generally required to be less than 5% (excluding crystalline water). The solvents carried by wet materials are usually flammable, explosive, toxic, and harmful hazardous chemicals, which are extracted by vacuum pump units during the drying process. There are two main types of vacuum pump units: wet and dry. The traditional wet vacuum drying system, due to the limitations of using wet vacuum pumps, not only cannot fully recover this part of the solvent, but also generates a large amount of wastewater and exhaust gas; This not only puts cost pressure on chemical pharmaceutical companies, but also poses challenges to health, safety, and environmental protection. By adopting a dry vacuum condensation system, it is possible to achieve complete solvent recovery and zero discharge of wastewater and exhaust gas.
2. The characteristics of organic solvents and their condensation methods
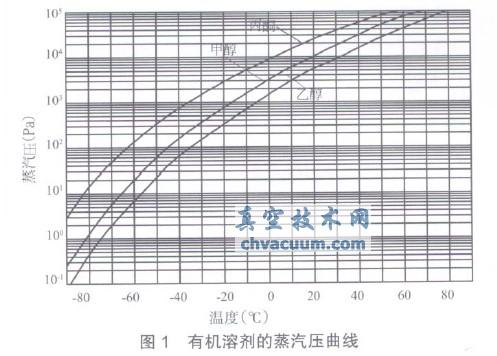
The commonly used solvents in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients are organic solvents such as methanol, acetone, ethanol, or other composite solvents. Their common characteristics are low boiling point and high saturated vapor pressure. For the drying process chain, there are usually two methods of condensation before and after the vacuum pump, also known as intake side condensation and exhaust side condensation, which require cooling the medium below the boiling point corresponding to the working pressure. The vapor pressure curves of several commonly used organic solvents (see Figure 1). From the curve, it can be seen that within the limit pressure range of the drying process (0.1~100 Pa), the boiling points of the three solvents are between -90 ℃ and -30 ℃, and deep cooling or cold trap condensation must be used. At atmospheric pressure (≤ 1.013 × 105Pa), the boiling points of the three solvents are between 56 ℃ and 78 ℃, and condensation can be achieved with only circulating water. Compared to the two, the conditions for exhaust side condensation recovery are the simplest and most economical.
3. Wet vacuum system
Wet vacuum systems generally use liquid ring pumps or liquid ring Roots vacuum pump sets. The sealing coolant of the liquid ring pump will dissolve or absorb some organic solvents during operation, which are divided into waste gas and high concentration organic wastewater (or waste liquid) in the gas-liquid separator, both of which need to be treated. There are various wet drying vacuum systems (as shown in Figure 2) based on the operating principle of wet vacuum pumps and the characteristics of organic solvents. The characteristics of each system are as follows:
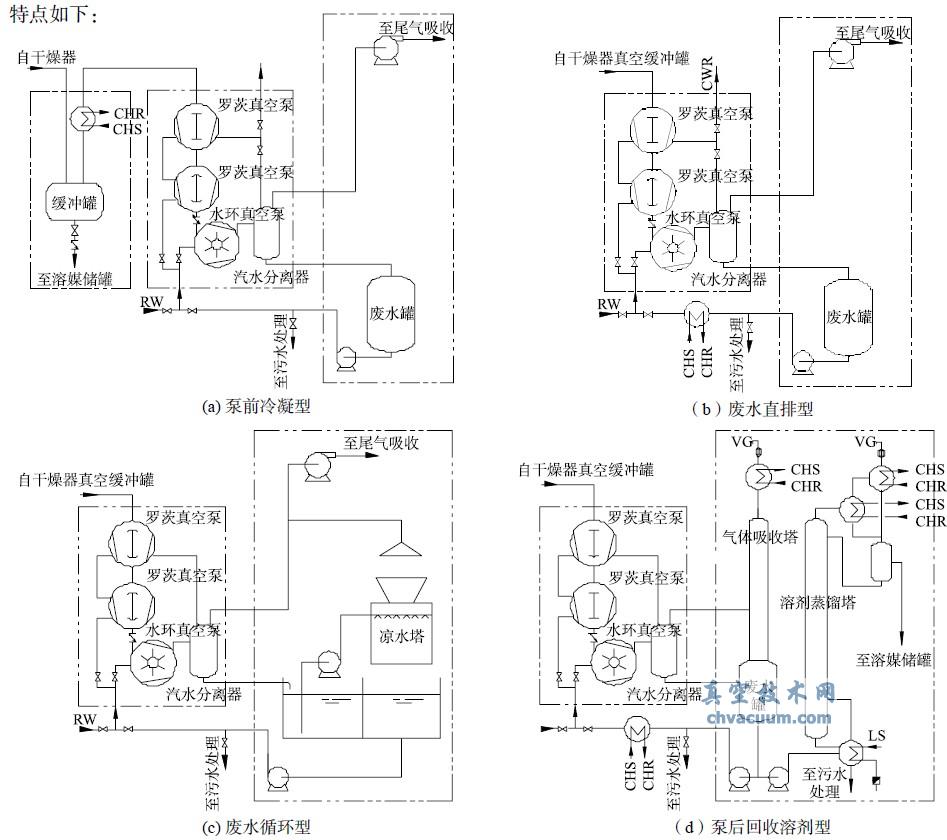
Figure 2 System flowchart of wet vacuum pump
(1) Pump front condensation solvent type (see Figure 2-a)
Add a condenser or cold trap in front of the pump to recover some solvent. Advantages: It recovers some solvents and improves the efficiency of the vacuum system. Disadvantage: It requires the configuration of deep cooling or cold trap, resulting in high investment and operating costs.
(2) Direct discharge type of wastewater (see Figure 2-b)
There is no treatment before or after the pump, and the wastewater is directly discharged into the sewage treatment device or outsourced for treatment. Disadvantages: High sewage treatment load, high water consumption, and high cost.
(3) Wastewater recycling type (see Figure 2-c)
The sealing liquid is used for cooling and recycling, and the dissolved saturated waste liquid is regularly treated. Advantages: Reduced water consumption. Disadvantages: Liquid ring pumps may experience cavitation and reduced efficiency, resulting in high waste liquid treatment costs.
(4) Pump recovery solvent type (see Figure 2d)
Distillation or membrane separation is carried out on the waste liquid to recover the solvent, and the waste liquid is cooled and recycled. Advantages: Recycling most solvents. Disadvantages: The recycling system has a large footprint, high energy consumption (especially distillation recycling), and high investment and operating costs.
From the above analysis, it can be seen that although various wet vacuum systems have been designed to recover solvents and reduce pollution emissions, the results are not satisfactory. This is determined by the characteristics of the solvent and the wet vacuum pump itself. Only by using a dry vacuum pump system and a matching condensation recovery system can this problem be completely solved.
4. Introduction to Dry Vacuum Pump
A dry vacuum pump is named after a liquid ring pump, where the working chamber of the pump does not require sealing of coolant. Due to the lack of sealing liquid and the exhaust pressure greater than atmospheric pressure, dry vacuum pumps can condense the discharged gas on the exhaust side.
Dry vacuum pumps include piston pumps, Roots pumps, claw pumps, and double screw pumps. The dry screw vacuum pump has the advantages of high operating efficiency, long service life, and low cost, and has gradually become the most widely used dry vacuum pump (see structure in Figure 3).
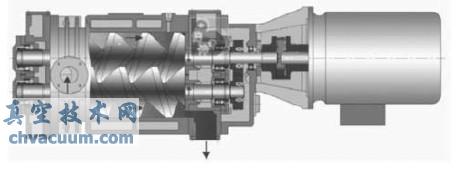
Figure 3 Structural diagram of dry screw vacuum pump
The rotor of a dry screw vacuum pump is a pair of screws with small gaps and no contact with each other. After changing speed through synchronous gears, it drives the gas to move towards the outlet. Its advantages are:
(1) Can operate at full speed under atmospheric pressure and extreme vacuum;
(2) A single stage can achieve a high degree of vacuum, and the ultimate pressure can be<10 Pa;
(3) There is no oil or water in contact with process gas in the working chamber of the pump;
(4) Rotors do not come into contact with each other, reducing wear and tear; The rotor can be coated with anti-corrosion coatings such as fluorine and nickel;
(5) The gas channel inside the pump is short, allowing for quick exhaust;
(6) It can be operated separately or as a front stage pump.
There are two types of dry screw vacuum pumps: equal pitch and variable pitch, also known as external compression screw and internal compression screw. Compared with equal pitch screws, variable pitch screw pumps have lower exhaust temperatures and higher efficiency.
5. Design of Dry Vacuum Condensation System
In recent years, dry screw vacuum pumps and exhaust side condensation have been applied in the pharmaceutical industry. Dry screw vacuum pumps, vacuum pipelines, and exhaust side condensation devices can be defined as dry vacuum condensation systems (see Figure 4 for the process). If influenced by factors such as design, selection, and special processes, there may be system mismatch, insufficient vacuum degree, and unstable operation. How to optimize the design and configuration of the system will be elaborated in the following text with engineering cases.
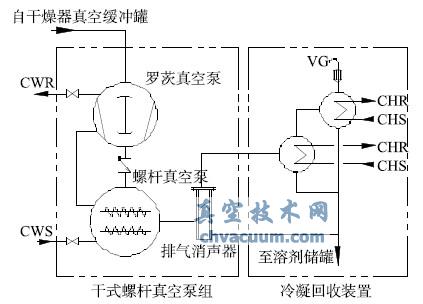
Figure 4 Flow chart of dry vacuum condensation system
conclusion
The application of dry vacuum condensation system can achieve the exhaust side condensation of organic solvents during the drying process, thereby achieving full recovery of organic solvents and zero discharge of wastewater and exhaust gas. Through system optimization design, the system has good compatibility, significantly reduces the maximum condensation load, and saves space. The dry vacuum condensation system can be applied not only in new projects, but also in retrofitting existing wet vacuum systems.

+86 10-64730110
+86 10-64730100