



Graphite, as a very common porous carbon material, has a wide range of applications in industrial production. Graphene, like graphene, carbon 60, carbon nanotubes, diamond, etc., are all called allotropes of carbon and are elemental elements of carbon.
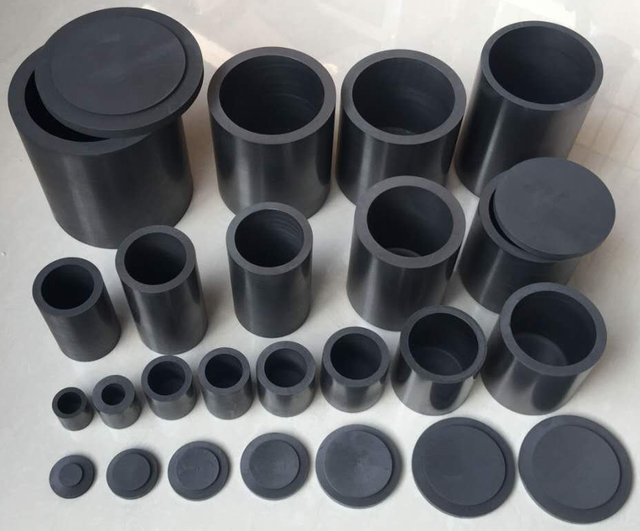

▲ Graphite is a gray black opaque solid
It is a mixed crystal with a density of 2.09 to 2.33g/cm3
Melting point 3652 ℃, boiling point 4827 ℃
Due to its unique sheet-like structure, graphite has stable chemical properties and resistance to acid, alkali, and organic corrosion at room temperature. It has good conductivity, thermal conductivity, lubrication, and high temperature resistance, and is widely used in industries such as chemical, photovoltaic, semiconductor, electronics, aerospace, and nuclear industry. Its application areas are mainly divided into the following aspects:
Used as refractory material: Graphite and its products have the properties of high temperature resistance and high strength. They are mainly used in the metallurgical industry to manufacture graphite crucibles. In steelmaking, graphite is commonly used as a protective agent for steel ingots and as a lining for metallurgical furnaces.
As a conductive material: used in the electrical industry to manufacture electrodes, brushes, carbon rods, carbon tubes, positive electrodes for mercury rectifiers, graphite gaskets, telephone parts, coatings for television tubes, etc.

Graphite is often used as a lubricant in the mechanical industry. Lubricating oil is often not suitable for use under high speed, high temperature, and high pressure conditions, while graphite materials can operate without lubricating oil at high sliding speeds at temperatures of 200-2000 ℃. Many devices that transport corrosive media widely use graphite materials to make piston cups, sealing rings, and bearings, which do not require the addition of lubricating oil during operation. Graphite emulsion is also a good lubricant for many metal processing (wire drawing, tube drawing).
Graphite has good chemical stability. Processed graphite, with characteristics such as corrosion resistance, good thermal conductivity, and low permeability, is widely used in the production of heat exchangers, reaction tanks, condensers, combustion towers, absorption towers, coolers, heaters, filters, and pump equipment. Widely used in industrial sectors such as petrochemicals, hydrometallurgy, acid-base production, synthetic fibers, and papermaking, it can save a large amount of metal materials.
Due to the porous structure of graphite materials, their mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, and other properties are affected. Therefore, we use impregnation technology to prepare impermeable graphite materials in the production process.
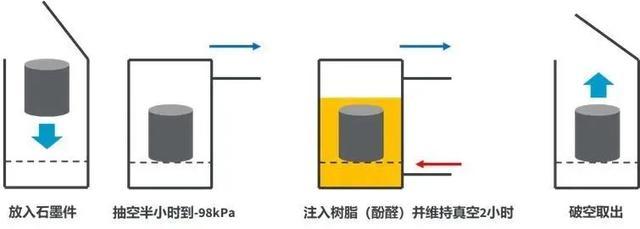
▲ Immerse the impregnating agent into the pores of graphite under a certain pressure
Improve the pore structure of graphite, optimize its strength and physicochemical properties
Common impregnating agents include synthetic phenolic resin, furan resin, tetrafluoro lotion, water glass, asphalt, etc. During the impregnation process, the vacuum environment helps to form smaller and more uniform pores, thereby improving the strength of graphite.
The preparation of graphite not only requires vacuum pump vacuum technology for impregnation, but also vacuum is essential in the pressing and forming process. When processing and producing graphite, it is usually necessary to press the graphite to form it and proceed with subsequent processing steps. In order to better shape graphite, a certain vacuum degree needs to be maintained in the space during graphite pressing. Graphite material can be added to the mold, and then the graphite in the mold can be pressed into shape through a pressure plate.
In addition, because graphite is a micrometer level powder material with extremely fine powder particle size, it is easy to ash during production and manufacturing, resulting in extremely harsh production environments, and material turnover has become very difficult. Traditional transportation methods no longer meet the requirements of large-scale production, and this type of dust transportation requires the help of vacuum feeding machines.

▲ Schematic diagram of vacuum feeding machine structure
The principle of negative pressure transportation using a vacuum pump takes up little space, and pipeline transportation is adopted during the transportation process, without the leakage of dust. Vacuum conveying has automated and dust-free the production of negative electrode materials, improving the production efficiency of graphite materials and reducing enterprise costs.
In the application of materials, graphite often cooperates with vacuum. For example, vacuum furnace graphite products that are increasingly widely used in vacuum furnaces. It can not only be used to manufacture heating components and insulation screens for vacuum furnaces, but also to manufacture load-bearing structural parts such as brackets, material trays, guide rails, bolts, bearings, fan blades, etc.
The application of graphite in vacuum furnaces greatly simplifies the design and manufacturing of vacuum furnaces, reduces the consumption of metals such as tungsten, molybdenum, tantalum, and stainless steel, lowers costs, improves certain performance of vacuum furnaces, and expands the scope of vacuum furnace use.

+86 10-64730110
+86 10-64730100